Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.69(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Shitade, Atsuo*; Araki, Yasufumi
Physical Review B, 103(15), p.155202_1 - 155202_8, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The axial magnetic effect (AME) is one of the anomalous transport phenomena in which the energy current is induced by an axial magnetic field. Here we numerically study the AME for the relativistic Wilson fermion in the axial magnetic field and a twisted Dirac semimetal. The AME current density inside the bulk is nonzero, and particularly in the low energy regime for the former model, it is explained by the field-theoretical results without any fitting parameter. However, for both models, the average AME current density vanishes owing to the surface contribution. The axial gauge field is regarded as the spatially modulated (effective) Zeeman field and induces the spatially modulated energy magnetization. The AME is attributed to the magnetization energy current and hence cannot be observed in transport experiments.
Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.38(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The soft nature of organic-inorganic halide perovskites renders their lattice particularly tunable to external stimuli such as pressure, undoubtedly offering an effective way to modify their structure for extraordinary optoelectronic properties. However, these soft materials meanwhile feature a general characteristic that even a very mild pressure will lead to detrimental lattice distortion and weaken the critical light-matter interaction, thereby triggering the performance degradation. Here, using the methylammonium lead iodide as a representative exploratory platform, we observed the pressure-driven lattice disorder can be significantly suppressed via hydrogen isotope effect, which is crucial for better optical and mechanical properties previously unattainable.
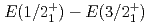 energy splitting in odd-K isotopes towards
energy splitting in odd-K isotopes towards 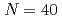
Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Duguet, T.*; Liu, H. N.*; Navr til, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 802, p.135215_1 - 135215_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:94.54(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ohdaira, Naoya*; Saito, Shigeru
Heliyon (Internet), 6(2), p.e03429_1 - e03429_8, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.81(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) is a candidate liquid metal coolant for a fast reactor, especially accelerator driven system (ADS). Freeze sealed valve is a candidate design to be possible to add passive safety to the reactor. On the other hand, since LBE is known that it causes expansion after its solidification, quantitative evaluation of the stress to the pipe produced by the LBE expansion should be considered. Many researchers produced related data for the expansion, however, evaluations of the strain by LBE expansion was barely reported. Therefore, the strain measurement using a stainless steel cup and the stress evaluation was performed together with visual observation using an optical microscopy. The results indicated keeping above room temperature (RT) was a significantly effective way to reduce the strain to the pipe.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 62(6), p.350 - 355, 2019/06
Thermal oxidation of Si substrate is an indispensable process for the Si device fabrication. However, the influence of oxidation induced strain cannot be ignored for thin films. Synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy was used as a method to measure simultaneously oxidation induced strain and oxidation rate. It was found that the acceleration of interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain was observed for the rapid thermal oxidation. The results can be explained by the model in which point defects caused by strain become reaction sites at the SiO /Si interface.
/Si interface.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Terada, Takaya; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Takehiro*; Shimomura, Takuya
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2014/07
Since 2007, JAEA has been developing laser based technologies of structural health monitoring. The FBG sensor made by femtosecond laser processing will be the best candidate. To make the best use of the heat resistant characteristic, the FBG sensor was embedded in metal mold by laser cladding. A groove was processed to the surface of a SUS metal plate. We used a QCW laser to weld a filler wire on the plate. A series of weld beads perfectly formed a sealing clad on the groove. Though the FBG sensor was buried tightly, no degradation on the reflection spectrum was detected after the processing. The FBG sensor could detect the vibration of the plate caused by impact shocks and audio vibration. The reflection peak of the FBG sensor under laser cladding condition was shifted to be 6 nm. We demonstrated that the corresponded temperature derive from the reflection peak shift reached 600 degrees in heat shock experiments. The installation procedure of a FBG sensor using a portable laser cladding machine was described.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kizu, Kaname; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Ando, Toshinari*; Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.922 - 925, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.95(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
 Al strand and cable-in-conduit conductor
Al strand and cable-in-conduit conductorKizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Shimada, Katsuhiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hishinuma, Yoshimitsu*; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yushi*; Nishimura, Arata*; Okuno, Kiyoshi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.872 - 875, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.95(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Hotta, Takashi
Progress in Ferromagnetism Research, p.19 - 38, 2006/00
In manganites, the appearance of the ferromagnetic (FM) metallic phase has been usually rationalized by the so-called double-exchange mechanism, based on a strong Hund's rule coupling between mobile 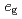 electrons and localized
electrons and localized 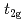 spins. Then, it has been believed for a long time that hole-doping is indispensable for explaining the FM metallic phase in manganites. However, it has been theoretically pointed out that a novel metal-insulator transition in the FM state can occur even for undoped manganites based on the
spins. Then, it has been believed for a long time that hole-doping is indispensable for explaining the FM metallic phase in manganites. However, it has been theoretically pointed out that a novel metal-insulator transition in the FM state can occur even for undoped manganites based on the 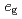 -orbital degenerate Hubbard model tightly coupled to Jahn-Teller distortions. In this article, the result is reviewed in detail.
-orbital degenerate Hubbard model tightly coupled to Jahn-Teller distortions. In this article, the result is reviewed in detail.

Johannsen, N.*; Vasiliev, A.*; Osawa, Akira; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Lorenz, T.*
Physical Review Letters, 95(1), p.017205_1 - 017205_4, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We present high-resolution measurements of the thermal expansion and the magnetostriction of TlCuCl which shows field-induced antiferromagnetic order. We find pronounced anomalies in the field and temperature dependence of different directions of the lattice signaling a large magnetoelastic coupling. The phase boundary is extremely sensitive to pressure, e.g. the transition field would change by about
which shows field-induced antiferromagnetic order. We find pronounced anomalies in the field and temperature dependence of different directions of the lattice signaling a large magnetoelastic coupling. The phase boundary is extremely sensitive to pressure, e.g. the transition field would change by about  185%/GPa under uniaxial pressure applied along certain directions. This drastic effect can unambiguously be traced back to changes of the intradimer coupling under uniaxial pressure. The interdimer couplings remain essentially unchanged under pressure, but strongly change when Tl is replaced by K.
185%/GPa under uniaxial pressure applied along certain directions. This drastic effect can unambiguously be traced back to changes of the intradimer coupling under uniaxial pressure. The interdimer couplings remain essentially unchanged under pressure, but strongly change when Tl is replaced by K.
Nishitani, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Tsutomu*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Okumi, Shoji*; Furuta, Fumio*; Miyamoto, Masaharu*; Kuwahara, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Naoto*; Naniwa, Kenichi*; Watanabe, Osamu*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 97(9), p.094907_1 - 094907_6, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:87.31(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Asaoka, Hidehito
KEK Proceedings 2004-5, p.52 - 53, 2004/08
no abstracts in English
Paul, N.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Voigtl nder, B.*
nder, B.*
Surface Science, 564(1-3), p.187 - 200, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.69(Chemistry, Physical)Using scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) the Ge epitaxy on a Bi terminated Si(111) surface is compared to the growth without surfactant. As soon as the 2 bilayer high wetting layer is completed with surfactant, Ge islands with a flat top and an underlying dislocation network occur. Elastic distortions due to the dislocation network result in periodic sub-Angstrom height undulations measured by the STM. In this case the Ge islands have the form of a mesa. With increasing Ge coverage, these mesas spread laterally. Beyond a Ge coverage of 10 bilayers, the Ge mesas have coalesced and further Ge deposition leads to a 2D layer-by-layer growth of Ge on Si(111). In epitaxy without the use of a surfactant as well, the formation of Ge islands with an underlying dislocation network is observed. However, in this case the Ge islands are much higher and show no tendency to coalesce. The partially relaxed islands coexist with another type of tall islands.
 Al conductor developed for JT-60SC
Al conductor developed for JT-60SCKizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hamada, Kazuya; Hara, Eiji*; Imahashi, Koichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1535 - 1538, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.57(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Paul, N.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Myslive ek, J.*; Voigtl
ek, J.*; Voigtl nder, B.*
nder, B.*
Physical Review B, 69(19), p.193402_1 - 193402_4, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:67.1(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We compare the initial stages of growth of Ge on Si(111) with Bi as a surfactant and without surfactant. At the beginning of growth, 3D islands with a strain relieving dislocation network at their base are formed in both growth systems. These islands can be regarded as seeds of a flat relaxed Ge layer on Si(111). However, such Ge layer forms at later stages of growth only in the growth with Bi surfactant, while the growing Ge layer without surfactant remains rough. What makes the dierence and the success of Bi surfactant mediated epitaxy is the lateral growth and coalescence of the seed islands that cover the entire surface within first 15 bilayers of Ge deposition. This happens due to a kinetic limitation of the incorporation of Ge into the growing layer in the presence of surfactant.
 crystal
crystalYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(4), p.1050 - 1053, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have observed 90 domain walls in a bulk BaTiO
domain walls in a bulk BaTiO crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO
crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90
multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90 domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO
domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
Hotta, Takashi; Moraghebi, M.*; Feiguin, A.*; Moreo, A.*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Dagotto, E.*
Physical Review Letters, 90(24), p.247203_1 - 247203_4, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:91.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Novel ground-state spin structures in undoped and doped manganites are here investigated based on the orbital-degenerate double-exchange model, by using mean-field and numerical techniques. In undoped manganites, a new antiferromagnetic (AFM) state, called the E-type phase, is found adjacent in parameter space to the A-type AFM phase. Its structure is in agreement with recent experimental results. This insulating E-AFM state is competing with a ferromagnetic metallic phase as well, suggesting that large magneto-resistant effects could exist even in undoped manganese oxides. For doped layered manganites, the phase diagram includes another new AFM phase of the 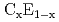 -type. Experimental signatures of the new phases are discussed.
-type. Experimental signatures of the new phases are discussed.
 -MO
-MO heterogeneous multi-phase systems (M=Ti, Nb, Si, V, etc.)
heterogeneous multi-phase systems (M=Ti, Nb, Si, V, etc.)Nakamura, Akio; Yoshii, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.160 - 163, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
 Al strand with high copper ratio of 4 for fusion magnets
Al strand with high copper ratio of 4 for fusion magnetsHosono, F.*; Iwaki, G.*; Kikuchi, Kenichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; Ando, Toshinari*; Kizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Sakasai, Akira
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 12(1), p.1037 - 1040, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.89(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English